According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer caused nearly 10 million deaths in 2020, accounting for approximately one-sixth of all deaths worldwide. The most common types of cancer in males are lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, stomach cancer, and liver cancer. For females, the most common types are breast cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, and cervical cancer.
Early detection, imaging diagnosis, pathological diagnosis, standardized treatment, and high-quality care have significantly improved the survival rates and quality of life for many cancer patients.
Pathological Diagnosis – The “Gold Standard” for Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment
Pathological diagnosis involves obtaining human tissue or cells through methods such as surgical resection, endoscopic biopsy, percutaneous puncture biopsy, or fine-needle aspiration. These samples are then processed and examined using tools such as a microscope to observe the tissue structure and cellular pathological features, which help in making a disease diagnosis.
Pathological diagnosis is considered the “gold standard” in tumor diagnosis and treatment. It is as crucial as the black box of an airplane, as it directly affects the determination of tumor benignity or malignancy and the formulation of subsequent treatment plans.
The Significance of Biopsy in Pathological Diagnosis
Pathological diagnosis is considered the gold standard for diagnosing cancer, and obtaining an adequate biopsy sample is a prerequisite for high-quality pathological testing.
Physical examinations, blood tests, urine tests, and imaging examinations can identify masses, nodules, or lesions, but they are not sufficient to determine whether these abnormalities or masses are benign or malignant. Only through biopsy and pathological testing can their nature be determined.
A biopsy, also known as a tissue examination, involves the surgical removal, forceps extraction, or puncture of living tissue samples or cell samples from the patient for pathological examination by a pathologist. Biopsy and pathological testing are usually performed to gain a deeper understanding of whether the lesion/mass is cancerous, the type of cancer, and its characteristics. This information is crucial in guiding subsequent clinical treatment plans, including surgery, radiation therapy, and drug therapy.
Biopsy procedures are typically performed by interventional radiologists, endoscopists, or surgeons. The obtained tissue samples or cell samples are examined by pathologists under a microscope, and additional analyses may be conducted using immunohistochemistry and other methods.
Technical Case
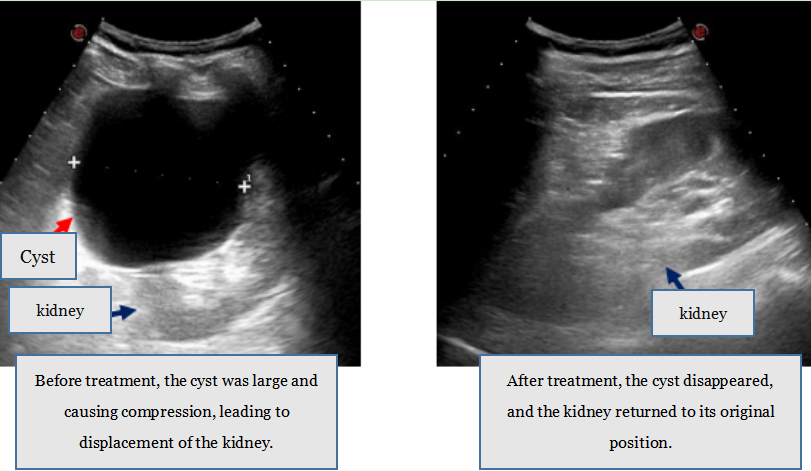
1. Cyst Sclerotherapy
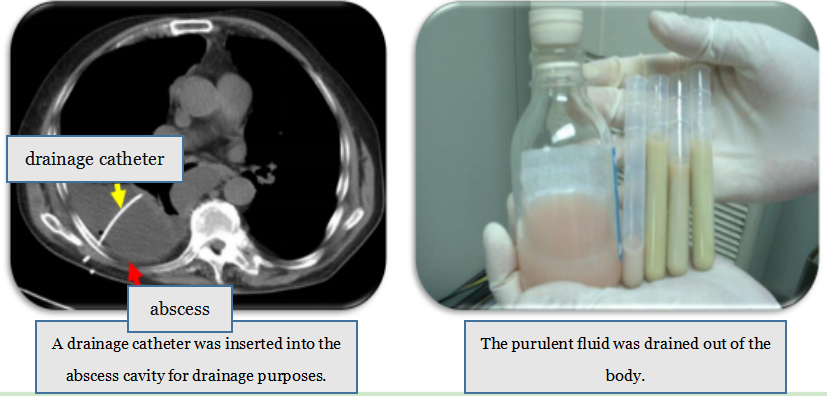
2. Abscess Drainage with Catheter Placement
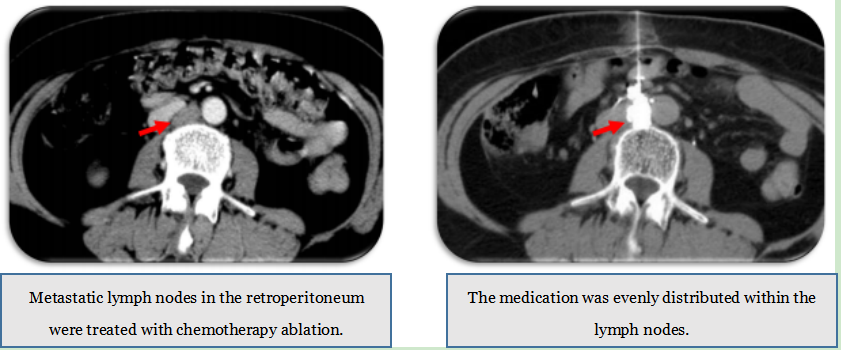
3. Tumor Chemotherapy Ablation
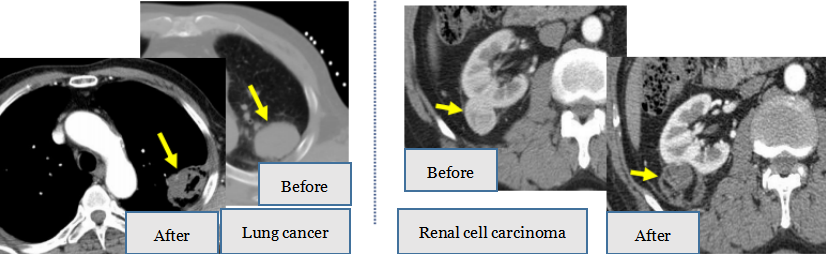
4. Solid Tumor Microwave Ablation
Post time: Jul-27-2023