What is CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell)?
First, let's take a look at the human immune system.
The immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body. One of the important cells involved are white blood cells, also called leukocytes, which come in two basic types that combine to seek out and destroy disease-causing organisms or substances.
The two basic types of leukocytes are:
Phagocytes, cells that chew up invading organisms.
Lymphocytes, cells that allow the body to remember and recognize previous invaders and help the body destroy them.
A number of different cells are considered phagocytes. The most common type is the neutrophil, which primarily fights bacteria. If doctors are worried about a bacterial infection, they might order a blood test to see if a patient has an increased number of neutrophils triggered by the infection.
Other types of phagocytes have their own jobs to make sure that the body responds appropriately to a specific type of invader.
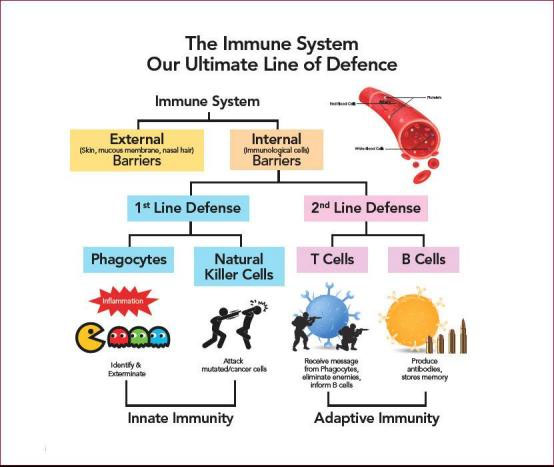

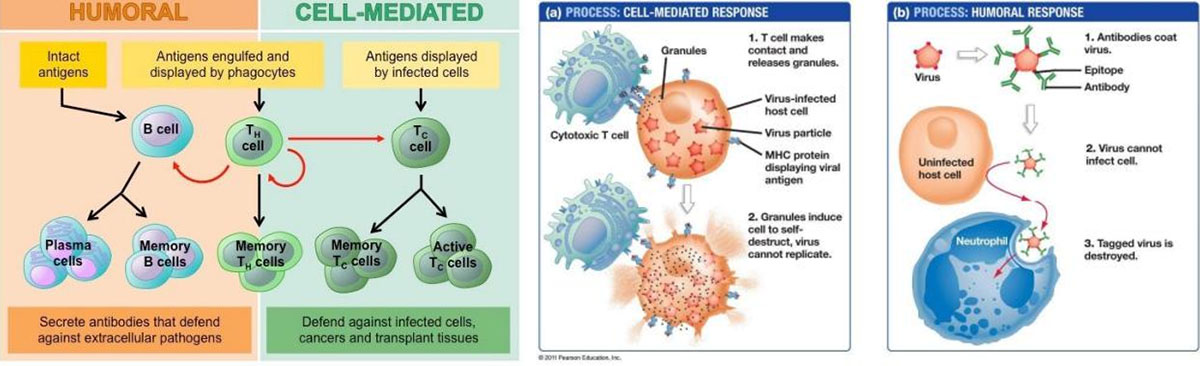
The two kinds of lymphocytes are B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. Lymphocytes start out in the bone marrow and either stay there and mature into B cells, or they leave for the thymus gland, where they mature into T cells. B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes have separate functions: B lymphocytes are like the body's military intelligence system, seeking out their targets and sending defenses to lock onto them. T cells are like the soldiers, destroying the invaders that the intelligence system has identified.
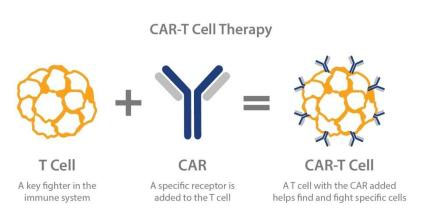
Chimeric antigen receptor(CAR) T cell technology: is a kind of adoptive cellular immunotherapy(ACI). Patient's T cell express CAR through genetic reconstruction technology, which make the effector T cells are more targeted, lethal and persistent than conventional immune cells, and can overcome local immunosuppressive microenvironment of tumor and break host immune tolerance. This is a specific immune cell anti - tumor therapy.
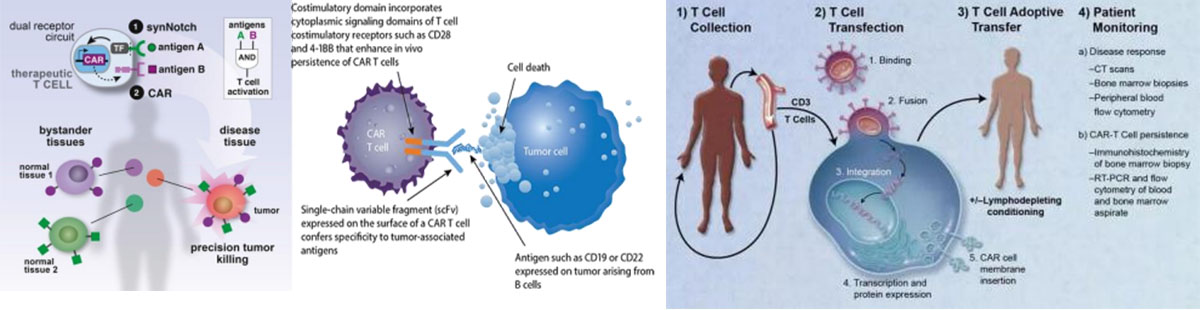
The principle of CART is to take out the "normal version" of the patient's own immune T cells and proceed gene engineering, assemble in vitro for tumor specific targets of large antipersonnel weapon "chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)", and then infuse the changed T cells back into the patient's body, new modified cell receptors will be like to install a radar system, which is able to guide the T cells locate and destroy cancer cells.
The advantage of CART at BPIH
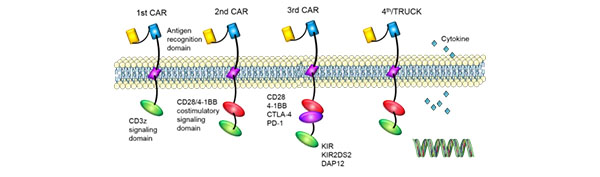
Due to the differences in the structure of intracellular signal domain, CAR has developed fourgenerations. We use the latest generation CART.
1st generation: There was only one intracellular signal component and the tumor inhibition effect was poor.
2nd generation: Added a co-stimulating molecule on the basis of the first generation, and the ability of T cells to kill tumors was improved.
3rd generation: Based on the second generation of CAR, the ability of T cells to inhibit tumorproliferation and promote apoptosis was significantly improved.
4th generation: CAR-T cells can be involved in the clearance of tumor cell population byactivating the downstream transcription factor NFAT to induce interleukin-12 after CAR recognizes the target antigen.
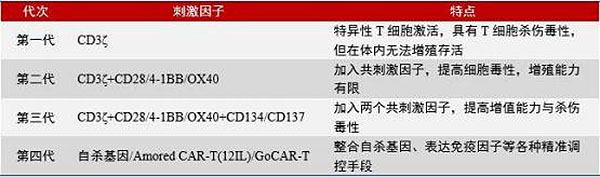
| Generation | Stimulation Factor | Feature |
| 1st | CD3ζ | Specific T cell activation, cytotoxic T cell, but could not proliferation and survival inside the body. |
| 2nd | CD3ζ+CD28/4-1BB/OX40 | Add costimulator, improve cell toxicity, limited proliferation ability. |
| 3rd | CD3ζ+CD28/4-1BB/OX40+CD134 /CD137 | Add 2 costimulators, improve proliferation ability and toxicity. |
| 4th | Suicide gene/Amored CAR-T (12IL) Go CAR-T | Integrate suicide gene, express immune factor and other precise control measures. |
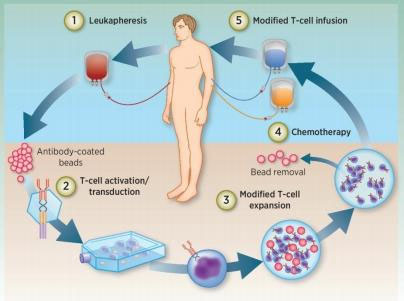
Treatment procedure
1) White blood cell isolation: Patient's T cells are isolated from the peripheral blood.
2) T cells activation: magnetic beads (artificial dendritic cells) coated with antibodies are used to activate T cells.
3) Transfection: T cells are genetically engineered to express CAR in vitro.
4) Amplification: The genetically modified T cells are amplified in vitro.
5) Chemotherapy: The patient is pre-treated with chemotherapy before T cell reinfusion.
6) Re-infusion: Genetically modified T cells infuse back into the patient.
Indications
Indications for CAR-T
Respiratory system: Lung cancer (Small cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma), nasopharynx cancer, etc.
Digestive system: Liver, stomach and colorectal cancer, etc.
Urinary system: Kidney and adrenal carcinoma and metastatic cnacer, etc.
Blood system: Acute and chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (T lymphoma excluded) etc.
Other cancer: Malignant melanoma, breast, prostae and tongue cancer, etc.
Surgery to remove the primary lesion, but the immunty is low, and recoery is slow.
Tumors with widespread metastasis that could not proceed surgery.
The side effect of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is big or insensitive to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Prevent tumor recurrenct after surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Advantages
1) CAR T cells are highly targeted and can kill tumor cells with antigen specificity more effectively.
2) CAR-T cell therapy requires less time. CAR T requires the shortest amount of time to culture T cells because it requires fewer cells under the same treatment effect. The vitro culture cycle can be shortened to 2 weeks, which largely reduced the waiting time.
3) CAR can recognize not only peptide antigens, but also sugar and lipid antigens, expanding the target range of tumor antigens. CAR T therapy is also not limited by the protein antigens of tumor cells. CAR T can use the sugar and lipid non-protein antigens of tumor cells to identify antigens in multiple dimensions.
4) CAR-T has a certain wide - spectrum reproducibility. Since certain sites are expressed in multiple tumor cells, such as EGFR, a CAR gene for this antigen can be widely used once it is constructed.
5) CAR T cells have immune memory function and can survive in the body for a long time. It is of great clinical significance to prevent tumor recurrence.
